Answer Keys
Lab 1 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Wear a lab coat and close-toed shoes.
Tie back long hair.
Any items from the safety agreement on page 5, including reading the lab ahead of time, knowing where safety equipment is, and keeping your work area clear of clutter. - Wash glassware. Wipe countertops. Wash hands.
- Because light passes through 2 lenses, you can see tiny things.
- Objective lens — Magnifies the image
Condenser — Focuses light on the specimen
Stage — What you place your slide on
Base and Arm — What you hold when carrying the microscope
Lab 1 Post-Lab Assignment
- With one hand supporting the base and one hand holding the arm.
- A fixed mount slide is a pre-prepared slide that is permanent. A wet-mount slide is made as needed and then dismantled or thrown away once used.
- Use the fine focus knob when on low power or high power. Use the course focus knob on scanning power and sometimes on low power.
- Answers will vary.
- An increase in magnification causes a decrease in the field of view.
Lab 2 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Diffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to a low one. Osmosis is the same type of movement, but specifically the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
- Semi-permeable means that some substances can cross and some cannot. We are using dialysis tubing as our semi-permeable membrane.
- Hypotonic, Hypertonic.
- To determine if substances have crossed the semi-permeable membrane.
- To keep the cell contents separate from its surroundings and regulate the entrance and exit of molecules.
Lab 2 Post-Lab Assignment
- The hot water had higher kinetic energy, causing the molecules to move faster.
- Answers will vary.
Mainly looking for some thought about comparing cells, tonicity, or consistency. - To determine if water entered or left the cell. To determine if a solution was hypo-, iso- or hyper-tonic.
- To see if glucose had left the “cell.” Because we already knew glucose was in the cell as we put it there.
- Answers will vary.
Possibly more pronounced results as cells had more time to reach an isotonic state through osmosis.
Lab 3 Pre-Lab Assignment
- S — The cell is replicating its DNA.
M — The cells are actively going through cell division.
G2 — The cell is making final preparations for cell division.
G1 — The cell is carry out regular cell processes. - Prophase → Metaphase → Anaphase → Telophase
- Mitosis results in 2 identical diploid cells, while meiosis results in 4 unique haploid cells.
- Synapsis and crossing over and independent alignment/assortment
- Meiosis 1 → Metaphase 1
Lab 3 Post-Lab Assignment
- Answers will vary.
The animal cells are round, and the plant cells are rectangular. The chromosomes in the plant cells look thicker vs. the thinner ones in animal cells. In animal cells, mitosis looks like a clear central line, while it looks a bit messier in plants. Students will often comment on the colour of the dye. - Answers will vary.
Students will either pick metaphase or anaphase. Either answer works as long as they relate the length of time to seeing the fewest of this stage through their microscope. - The drawing should show chromosomes aligned at the equator. The drawing should include a rectangular cell wall for the plant cell and a round cell membrane for the animal cell. Encourage students to draw what they saw, not what their diagrams look like.
- Answers will vary.
Lab 4 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Epithelial — Forms linings and coverings
Connective — Cells in a non-cellular matrix
Muscular — Is contractile
Nervous — Conducts electrical impulses - Atom → Molecule → Cell → Tissue → Organ
- Tissue is a group of specialized cells working together to perform a specific function. This branch of science is histology.
- Yes.
Lab 4 Post-Lab Assignment
- Epithelial cells have a free surface and a basement membrane. Half marks for “forms linings and coverings.”
- The loose fibrous connective tissue has open spaces between the cells and between protein fibres. The dense fibrous connective tissues are made of densely packed parallel strands of fibres, with no extra spaces between them.
- Osteocyte — Supportive connective/bone
Intercalated disc — Cardiac muscle
Chondrocyte — Supportive connective/cartilage
Leukocyte — Fluid connective
Neuroglia — Nervous
Collagen & elastin — Fibrous connective
Goblet cell — Epithelial
Peristalsis — Smooth muscle - Answers will vary but must include visual characteristics.
May talk about the shape and layering of cells, type of matrix (fibres, bone, cartilage, fluid), striations, and relative size of cells.
Lab 5 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Chemoreceptor — Presence of chemicals
Photoreceptor — Presence of light
Thermoreceptor — Change in temperature
Mechanoreceptor — Movement/pressure - Central nervous system (CNS). Peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- Sensory input, interpretation/integration, and motor output.
- Fight or flight. Rest and digest.
- Neurons and neuroglia (glial cells).
Lab 5 Post-Lab Assignment
- Brain and spinal cord
- Answers will vary.
Can include size (sheep smaller), shape (sheep elongated), and position of the brain stem (sheep exits the brain at an angle more to the dorsal side). - Answers will vary.
Should discuss age, gender, and eye health. - Answers will vary.
Should talk about the density of receptors in different areas of the dermis.
Lab 6 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Osteocytes. Bone marrow.
- Axial — Ribs, spine, and skull
Appendicular — Leg, arm, and shoulder - Sinus — A cavity or open space
Condyle — A rounded bump where a bone meets another bone
Foramen — A hole or opening
Diaphysis — The middle portion of a long bone - Proximal. Medial. Inferior.
Lab 6 Post-Lab Assignment
- Answers will vary.
Should mention that the ball on the femur is extended, and on the humerus, it sits directly atop the bone.
Should talk about range of motion and/or weight-bearing function. - Answers will vary.
The tibia is much thicker and has a flattened space on the proximal end for the femur to articulate.
The fibula is much more slender. - Femur — Large ball on the proximal end
Cervical vertebrae — Large central foramen and two smaller transverse foramen
Patella — Small oval-shaped bone found at the knee
Sacrum — Curved triangular-shaped bone with several pairs of foramen - Ossicles of the inner ear. Femur.
Lab 7 Pre-Lab Assignment
- The AV valves sit between the atria and ventricles and have chordae tendineae supporting them. The semilunar valve sits at the exit of the ventricles and has no chordae tendineae.
- Epicardium — Connective tissue
Myocardium — Cardiac muscle tissue
Endocardium — Epithelial tissue 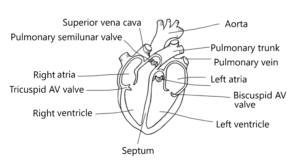
Lab 7 Post-Lab Assignment
- The tricuspid valve had three cusps and three points of attachment for the chordae tendineae, which are much smaller. The bicuspid valve had two cusps and two points of attachment, and the chordae tendineae were much larger.
- The myocardium of the left ventricle was much thicker than that of the right ventricle.
- These went directly back to the heart tissue. The purpose of these coronary arteries is to provide high-oxygen blood to the myocardium.
- The aorta was much stretchier to accommodate for fluctuations in blood pressure due to the pumping of the left ventricle.
- The left ventricle because it has to be strong enough to pump blood to the entire body.
Lab 8 Pre-Lab Assignment
- Erythrocyte — A red blood cell
Antigen — A glycoprotein projecting from the surface of a red blood cell
Antibody — A protein created by the immune system that targets and destroys a specific antigen
Agglutination — Clumping of blood cells caused by exposure to an antibody - The blood type is A+. Antibodies are Anti-B
- To avoid agglutination, which can kill the patient. Agglutination and death.
- Blood typing. We expose an individual’s blood to each antibody type and watch for agglutination. If agglutination occurs to a specific antibody, we know that that type of antigen is present.
- Blood type B+. Can receive B+, B-, O+, O-.
Lab 8 Post-Lab Assignment
-
Patient Response to Anti-A Response to Anti-B Response to Anti-Rh Blood Type Mr. Smith Mr. Jones Ms. Brown Mr. Green
2.
3.
4.

